Nautilus Marine Service

Housings
VITROVEX® by NAUTILUS MARINE SERVICE GmbH
Nautilus Marine Service is a German-based specialized company to manufactures pressure housings made of glass (VITROVEX) for use in the deep sea. The company was founded in 1985 and has been investing continuously in people and technology to maintain technical leadership in the products on offer. Nautilus Marine Service is closely associated with regional distributors around the world and exports over 90% of its VITROVEX glass products to more than 30 countries. All well-known marine research facilities are among these customers.


Nautilus Marine Service pursues long-term goals and partnerships with its customers, employees, and business partners and acts sustainably in accordance with the best interests of its customers without losing sight of its long-term viability. The main product range of the company Nautilus Marine Service is floatation and instrument housings made of glass under the brand name VITROVEX. VITROVEX glass belongs to the group of borosilicate glasses, which are characterized by their low sensitivity to temperature changes (due to the low-temperature expansion) and their high resistance to chemical agents.
As of March 25th, 2019 the customs tariff no. for all VITROVEX pressure housings has been set to 9015 9000.


Nautilus Marine Service operates its own fully computer-controlled pressure test facility (ID 700mm, length 1400mm) in which all pressure housings can be tested up to 1300bar.In ocean research and exploration, pressure housings are often acquired in small quantities and only after intensive consulting talks upfront to capture customer-specific requirements and support decision-making. The provision of these services in combination with the wide range and variability of the products makes Nautilus Marine Service special and unique. A fact that was also honored with the awarding of the Compass International Award 2015 and in turn, motivates all employees of Nautilus Marine Service to continuously strive for the highest quality and reliability of products, services, and work processes.
BENEFITS
Benefits of VITROVEX® glass enclosures in Ocean Exploration
All stationary and autonomous instrumentation for observational activities in ocean research has two significant things in common. Firstly, they require pressure-resistant housings, and secondly, they need buoyancy to bring instruments safely back to the surface. The use of glass housings is naturally attractive for meeting both these requirements.
Glass is one of the most difficult materials to work with because glass melt is infernal hot and cannot be hand-crafted. Nevertheless, making products out of glass has been a temptation that is obviously impossible to resist for 3000 years.
VITROVEX® glass enclosures show very little deviation in shape even under very high pressure. In addition to excellent molding of the highest quality glass, skilled craftsmanship ensures high manufacturing precision with extremely low tolerances.
Distinguishing features of VITROVEX® glass housings are:
- Immense strength-to-weight ratio
- Highly resistant to breaking (low thermal expansion coefficient)
- Inherently inexpensive
- Corrosion-resistant, Non-polluting, and ecologically acceptable
- Remarkable transparency and clarity with smooth, pore-free surface
- Parting plane sealing faces are honed to a precise flatness and finish
- Non-magnetic and electrically non-conductive
- hemispheres are interchangeable and individually replaceable
- For protection, storage, and ease of handling LDPE (low-density polyethylene) protective shells are available as well as a mounting framework with swiveling sphere fixings, rope, thimbles, and shackles
(EDDYGRIP system) - The serial number and production period are indicated on each hemisphere
INTERESTING FACTS
A few general considerations about glass…
Glass got its name from the Old Germanic word for amber: “glasa” – the shining or shimmering. However, there are no chemical and physical relationships between them, except for both being solid liquids. Solid and liquid: yes, a contradiction, indeed!
Academics are still debating today whether glass is solid or liquid. Thus, depending on your point of view, get yourself comfortable with one of the definitions below:
Glass is
- …an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as hard, brittle, and
impervious to the natural elements. Glass has been made into practical and decorative objects since
ancient times, and it is still very important in applications as disparate as building construction,
housewares, and telecommunications. It is made by cooling molten ingredients such as silica sand with
sufficient rapidity to prevent the formation of visible crystals. (source: Encyclopædia Britannica) - …structurally a solid, non-crystalline material.
- …physically a frozen, supercooled liquid.
- …chemically an amorphous mixture of basic and acidic oxides.
As consensus in the scientific world, glass can be understood as a melt solidified without substantial crystal formation, i.e. glass is an amorphous solid or an x-ray amorphous substance. Thermodynamically, glass is a frozen, supercooled melt or a liquid, with infinite toughness.And, precisely the contradictory forms of appearance – fluid, translucent, magically shimmering yet brittle, cool, and fragile – make this material so fascinating to work with.
Glass is copied from nature…
Glass as such is not an invention of humankind but rather copied from nature. Natural glass may emerge from volcanic eruptions (obsidian), meteorite impact (tektites and dialectic glass), and lightning strikes (fulgurites). Astronauts found natural glass on the moon, most likely formed by meteorite impacts.
There are no exact details about the origin of glassmaking. From sand (with a high concentration of limestone) in conjunction with soda, glass was probably coincidentally produced as a random product when firing pottery and as a colored glaze on ceramics.
Findings prove that Egyptians, Babylonians, and Assyrians have already been able to melt glass. The oldest finds date back to 7000 years BC. About 3000 BC, Egyptians already made aesthetic and practical objects for daily use from glass.
The old recipe “Take 60 pieces of sand, 180 pieces of seaweed ash, 5 pieces of chalkstone – and you’ll get a glass.” is still valid today. That recipe was found carved in cuneiform on a clay tablet as part of the library of the Assyrian king Assurbanipal in Nineveh from the year 650 BC.
A formerly completely opaque mixture becomes one of the most fascinating materials
Glass is a mixture in which the constituents cannot be described by a single chemical formula. In the narrower sense, glass is primarily a solidified inorganic melt based on silicon dioxide (SiO2), i.e. primarily made of quartz sand and additives such as soda (sodium carbonate, Na2 CO3 – in the past also potash (potassium carbonate, K2CO3), manganese oxide and metal oxides.
Since all these raw materials are abundant in nature, glass is already a highly environmentally friendly and versatile material.
The properties of a glass are defined by its chemical composition. By varying the ingredients and their relative amounts, glass can be designed for almost any intended purpose with regard to its mechanical or thermal strength or optical properties. In general, three main groups can be identified which make up for approx. 95% of the total glass production:
- soda-lime glass,
- borosilicateglass and
- lead glass commonly called crystal.
VITROVEX glass housings are made of borosilicate glass, which is characterized by its low sensitivity to temperature changes (due to the low-temperature expansion) and its high resistance to chemical attack. Borosilicate glass has a higher proportion of silica than soda-lime and leads glasses and its name comes courtesy of the proportion of boron oxide. Borosilicate glass is very often used in the chemical industry and in laboratories but is also widely used in households as a “refractory glass” (Jenaer Glas) and, because of the high thermal shock resistance, as fire protection glass.
Making of VITROVEX glass (products)…
By using elaborate methods, a batch of raw materials (silicon oxide, boron oxide, sodium/potassium oxide mix, and aluminum oxide) together with a proportion of cullet is mixed up and melted at a temperature of approximately 1600 °C in which the melting aggregates are heated electrically and operated around the clock.
After a period of refining, in which gases in the melt are expelled and the following standing time, in which the material is cooled but remains still very hot (just below 1600°C), the viscous mass of glass can be further shaped. By means of a cooled, hydraulic-driven stamp, the liquid glass is forced into a mold and pressed into the desired VITROVEX hemisphere. All this must be done within very few minutes until the material solidifies and make it impossible to be further processed.
Therefore, years of experience and practice are necessary to achieve appropriate glass qualities.
During shaping, mechanical stresses occur in the glass as a result of differences in strain. The occurring thermal stress depends on the expansion coefficient and is reduced by defined slow cooling (annealing) in a dedicated cooling zone. The time required to run through the cooling line is between 30 minutes and 100 minutes for our VITROVEX glass components depending on the diameter and wall size.
As an aside, for large optical lenses of 1m diameter and more, slow cooling of over one year or more may be necessary to avoid mechanical tension because even the tiniest deformations can result in blurring or image distortion. Similar annealing periods would be expected for hemispheres large enough to accommodate human beings.
At the end of the glass manufacturing process is the refinement, i.e. a possible polishing, etching, or engraving.
REFERENCES
Nautilus Marine Service has a high degree of familiarity in Germany as a trading specialist for marine safety equipment and oceanographic/hydrographic products, and abroad as a subsea developer of very high-pressure resistant glass enclosures for instrument housings and buoyancy (VITROVEX).
Thanks to the many years of experience in the aforementioned business areas, Nautilus Marine Service stands for expertise and confidence in the products and services offered and has gained a broad national and international customer base including companies, institutions, and individuals across the entire spectrum of the maritime industry.
Nautilus Marine Service is closely associated with regional distributors around the world and exports over 90% of its VITROVEX glass products to more than 30 countries. All well-known marine research facilities are among these customers.
The provision of excellent services in combination with the wide range and variability of products was honored with the awarding of the Compass International Award 2015 by the Marine Technology Society.
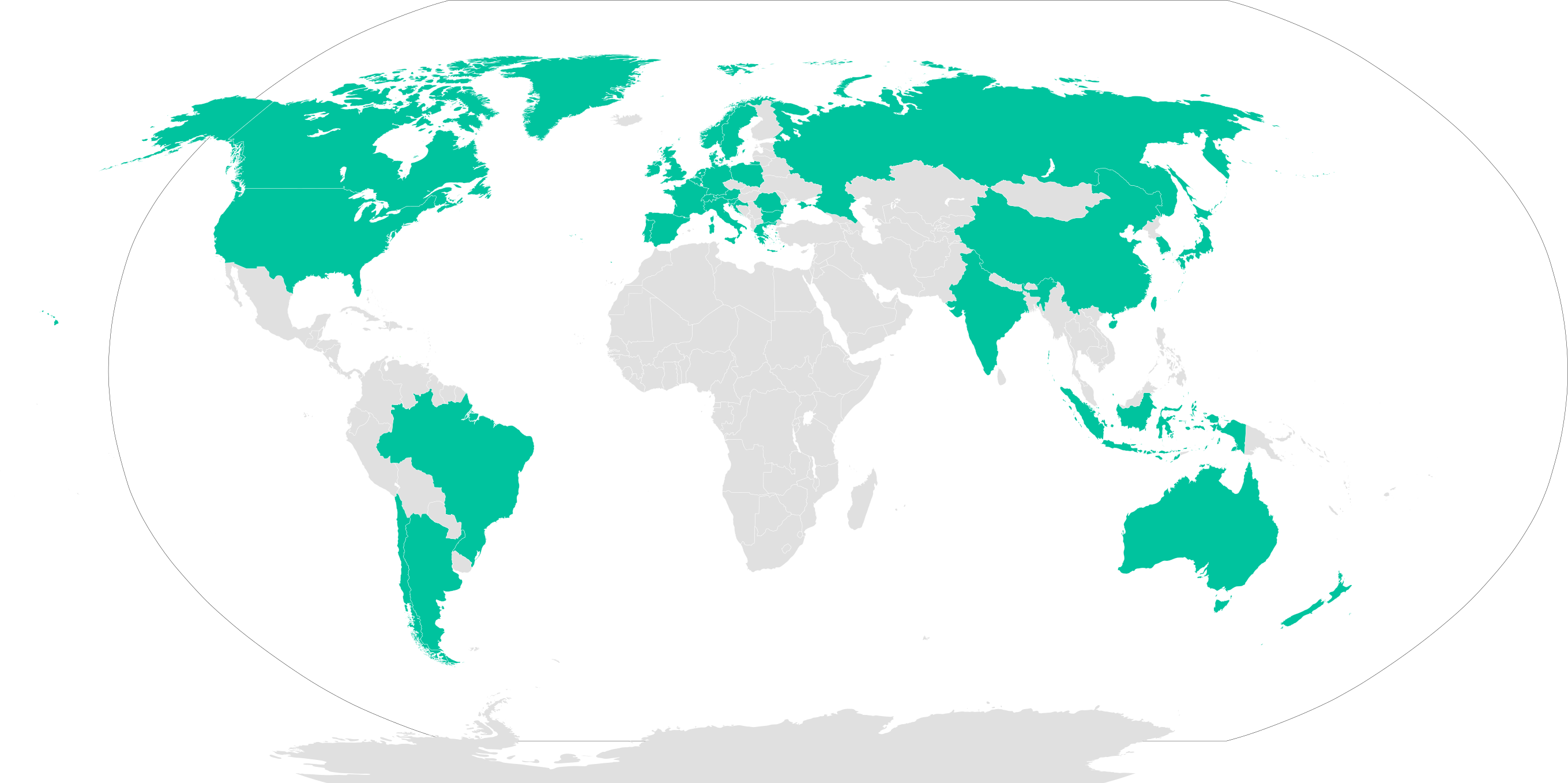
VITROVEX glass products are used in more than 30 countries (green)