Galvanic series of metals in seawater
The table shows how the various metals are been denoted noble and less noble.
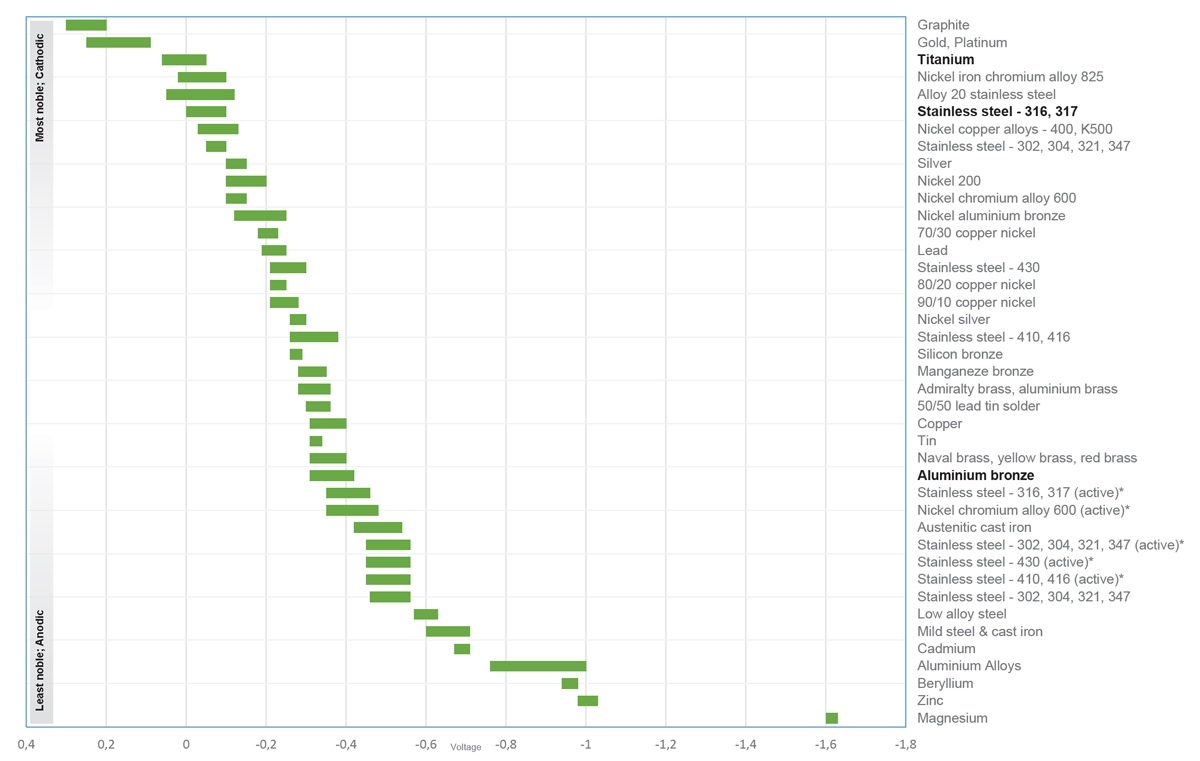
- *Ranges in acidic water, e.g. in crevices, stagnant, low velocity or poorly aerated water
- The closer 2 metals in the table are to each other, the less prone they are to corrode
- The further away 2 metals in the table are, the greater the risk of corrosion of the less noble (anode)
- The higher the potential the more noble a specific material will be
Example:
– Stainless steel AISI 304 is more noble than aluminum
– Stainless steel AISI 316 is more noble than AISI 304
– Titanium of any grade is more noble than AISI 316
CONTACT US FOR MORE INFO